
Mankind had its origins in nature and has relied on, developed and matured in it in the process of evolution. The fact htat many people now live a prosperous life is the result of advantageous utilizationof the natural environment. Natural history is the study of this interaction between mankind and the natural environmentt and the consequent process of environmental change. As a result, understanding natural history is important not only on a purely scientific basis but because of its social and environmental ramifications.
The exhibits, which have been established in harmony with each other, amount to approximately 2200 items and fill an area of 1484 m2, the space of the exhibition area of the permanet hall. The natural history portion displays exhibits dealing with "the creationof the universe to the time of man" as well as "Korea's nature". The astronimical departments include information about the origin and evolutionof the universe, galactic systems and solar system. The anthropology section comprises of information concerning the origin of life, the evolutional development of mankind, the Allosaurusdinosaur, etc. The first portionof the Korea's nature department deals with the abiotic environment, including fossils, mineral resources, and rocks. In the second half, the biotic environment such as mammals, reptiles, amphibians, birds, fisheds, invertebrates, angiosperms, gymnosperms, parasitic plandt, insectivores, and medical palnts are presented.
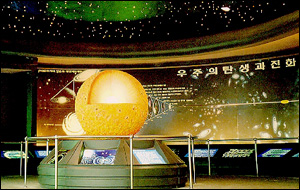
The universe came into being at the Big Bang approximately 15 billion years ago. At the beginning, there were extremely high densities and temperaturesin a state of chaos with no distinction among space, time, and matter. During the Big Bang, neutrons, atoms, electrons etc. were formed. In their interaction with each other, helium and hydrogen were created. The evolution of helium and hydrogen played an important part in the formation of the galactic systems which includes the Milky Way. Our solar system is one out of many galactic systems. The earth, on which man lives, is the third palnet in the solar system.
  |
|
Geological time is divided into the precambrian, paleozoic, mesozoic, and cenozoic eras.
The precambrian era began with the occurrence of primitive algae and fungilike prokaryotes.
Invertebrates and vascular plants, reptiles and gymnosperms, mammals and angio sperms characterized the paleozoic, mesozoic and cenozoic eras respectively. The first ancestor of man emerged in the last period of the cenozoic era.
|
Theee geology and mineralogy sectiob shows rocks, fossils, geological stratum, and the formative process of the Korean peninsula. Many fossils of the animals and plants which lived from the paleozoic to the cenozoic era are exhibited. The ingabitants in the Bronze Age (around B. C. 1000) are belieced to have used the new metal-working technology. Fullfledged farning staeted in the Bronze Age. The iron culture, introduced around the fourth century B. C. deeply influenced the ingabitants


|
  The zoology section displays mammals, birds, reptiles, ampibians, fishes, invertebrates including insects, and others which are known to Korean fauna. |
 
|
 |
 |
The Botany department presents dioramas of various plants such as gymnosperms, angiospeerms, medical plants, parasitic plants, insecitvorous plants, etc.