

 History
History
The Ministry of Legislation was founded at the same time as the Government of the Republic of Korea was established, and whenever the constitutional government system was varied, its status has changed slightly as follows:
(1) Start as the Ministry of Legislation
At the time the Government of the Republic of Korea was established in August 15,1948, the Ministry of Legislation started its functions with one office, three bureaus, ten divisions and a library, by taking over the Drafting Bureau, Law Research Bureau of the Interim Government of South Korea which was then a provisional governmental organization. It was one of the central administrative agencies under the jurisdiction of the Prime Minister as at present it is, and the Minister of Legislation was not a member of the State Council, but was entitled to attend and speak at any meeting of the State Council.
(2) Reorganization as the Legislation Office under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Justice
In November 29, 1954, as the Prime Minister system was abolished due to the amendment of the Constitution, the name of the Ministry of Legislation was changed into the Legislation Office under the jurisdiction of the Minister of Justice, with the status of an independent central administrative agency maintained. The chief of Legislation Office then was equivalent to the Minister, and was entitled to attend and speak at any meeting of the State Council as before.
(3) Reorganization as the Legislation Bureau of State Council Secretariat
As the Cabinet government system was in operation in June 15, 1960 in accordance of the amendment of the Constitution, and all the executive power was concentrated in the State Council, the State Council Secretariat was set up newly for the purpose of enabling the Prime Minister to exercise effectively his authority directing and controlling the ministries of the Executive Branch, and consequently the Legislation Office of the Ministry of Justice was reorganized as the Legislation Bureau of the State Council Secretariat.
(4) Restoration to the Ministry of Legislation
In December 26, 1962, as the presidential government system was restored according to the amended Constitution, the Ministry of Legislation resumed the status as a central administrative agency under the jurisdiction of the Prime Minister, and such a status continues up to now.
 Organization
Organization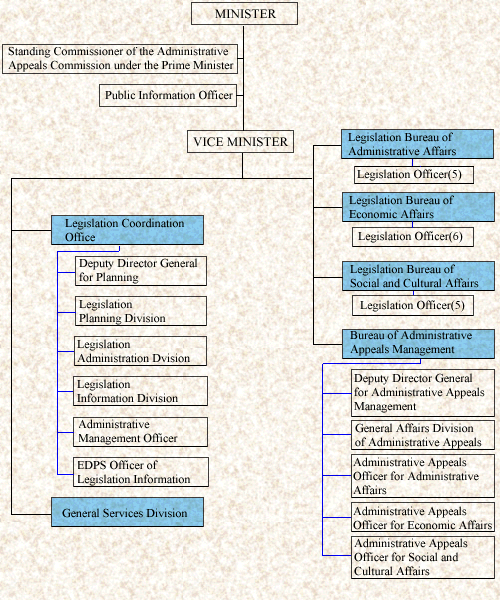
 Functions
FunctionsThe Ministry of Legislation is responsible for the establishment of policies on legislative administration of the government in general; coordination of the government legislation; review of bills of laws, treaties, etc; authoritative interpretation of laws and regulations; operation of the Administrative Appeals Commission under the Prime Minister; research and analysis of legislative information; public information on laws and regulations; support to legislative activities for local governments.
| Agency Name | Major Functions |
|---|---|
| Legislative Coordination Office | General Control over and Coordination of the
Government Legislation.
Presentation of Bills of Laws and Regulations before the State Council Authoritative Interpretation of Laws and Regulations Submission of the Executive's Legislative Bills to the National Assembly, and Preparation of the Promulgation of Laws and Regulations Planning and Coordination of Major Program Budgeting and Control over Expendture Research and Study of the Domestic and Foreign Legislation Information Compilation, Publication and Dissemination of Laws and Regulations Electronic Data Processing of Legislation Information |
| Legislation Bureau of Administrative Affairs | Reviewing and Drafting of Legislative Bills of the
Ministries mainly in charge of the General Administration
Authoritative Interpretation of Laws and Regulations |
| Legislation Bureau of Economic Affairs | Reviewing and Drafting of Legislative Bills of the
Ministries mainly in charge of the Economic Affairs
Authoritative Interpretation of Laws and Regulations |
| Legislation Bureau of Social and Cultural Affairs | Reviewing and Drafting of Legislative Bills of the
Ministries mainly in charge of the Social, Cultural
Affairs
Authoritative Interpretation of Laws and Regulations |
| Bureau of Administrative Appeals Management | Operation of the Administrative Appeals Commission under the Prime Minister |
| Public Information Officer | Public Information of Important Laws and Regulations Related to the Citizen's Daily Life |
| General Services Division | Personnel and General Affairs, Accounting |