
 |
|
 |

| An LSI (large-scale integrated circuit) is an electrical component consisting of hundreds of thousands of resistors, transistors and other circuit elements on a thin semiconductor wafer only a few millimeters square. LSI's are used in computer operating logic circuits and memories. |
|
LSI is an integrated component in which innumerable parts are incorporated into a single semiconductor. |
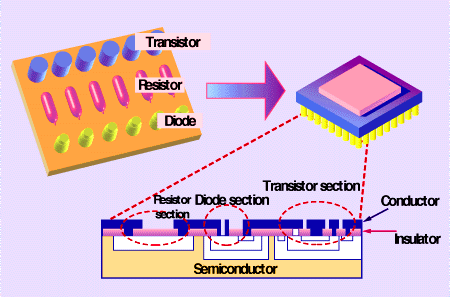 |
| Why Do We Use LSI's?
LSI's offer many advantages. They make it possible to reduce size and weight. And they use less electricity. Because they combine many components in one chip, they reduce the amount of soldering needed to make connections, and they increase reliability. Also, because LSI's are smaller they can transfer signals faster, and thereby increase performance. In addition, they can be mass produced so that they cost less. |
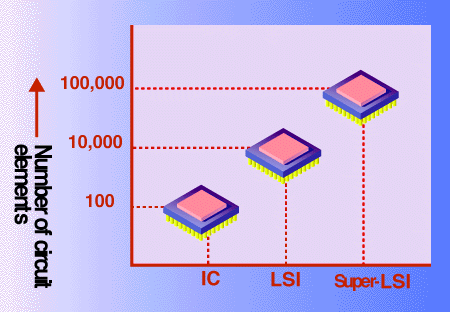 |
| How Do We Use LSI's? |
Many logical circuits can be combined on an LSI for processing software commands and mathematical calculations. |
Large amounts of data such as programs and results of computations can be stored in memories. The various types of memories include RAM which allows data to be written and read at any time, and ROM which allows reading only of information stored at the time of manufacture. |
|

|
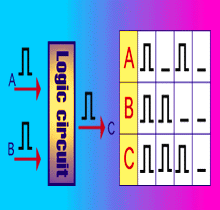
| This example shows a circuit that accepts input at either A or B, and produces output at C. The one-chip microprocessor includes all of the components that control a computer on a single chip. | The newest 1-megabit (1,000,000 or more gates) LSI's have memory capacity for about 128,000 letters or numbers on one chip, or enough for seven pages of a newspaper. |
| What Are LSI's Used In? LSI's are used in computers, of course, as well as TV, stereo and other electronic products. In electronic communications systems, they are also used in switching equipment, faxes and other applications. |
| Computer | Stereo | Facsimile | Electronic organizer | Calculator |
 |  |  |
 |
 |


|
Return to the Gakushukan Home Page | ||
|
Back | Forward |
|