 |
 |


(PMC Service Experiment) |
 |
 |
 |


(PMC Service Experiment) |
 |
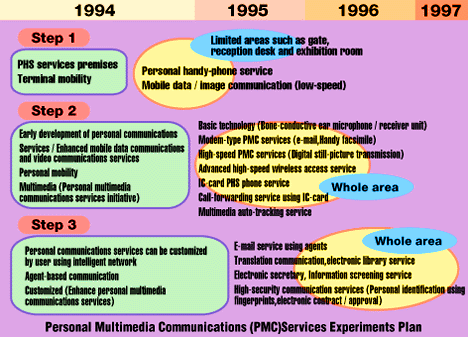
In the step 1 experiment (early development of PHS services premises) which was started last year, were tested terminal mobility such as propagation characteristics of PHASE radio section at the Mutation Research and Development Center. Step 2, started this April, is the beginning point of multimedia aspect of personal communication experiments.
Although the words "personal communication" remind us of NTT's concept "my wireless telephone", meaning of the words in the context of VI&P is that VI&P includes the concept of my "favorite service" which refers to custom-made services. Therefore, wired networks are also included in networks which offer personal communication services. Step 2 is divided into two parts. One is terminal type PMC services, which include services incorporating PHS terminals and non-telephone terminals. The other part is network-type PMC services, which include services incorporating PHS terminals and wired intelligent networks.
Terminal-type PMC services are multimedia communication services and have the following advantages.
As for network-type PMC services, the PHS network can detect location information of people using PHS terminals or wireless IC cards, which contain stored personal user's numbers. The range of the terminal is several hundred meters. By using the location information, the network-type PMC service can provide some custom-made services such as call-forwarding. It is possible to access a user who has a wireless IC card by calling his personal number. Although terminal mobility, has already been achieved with the conventional cellular phone, we have achieved personal mobility with the network-type PMC services.
