[Organization Framework and Legal Framework]
Organizational Framework
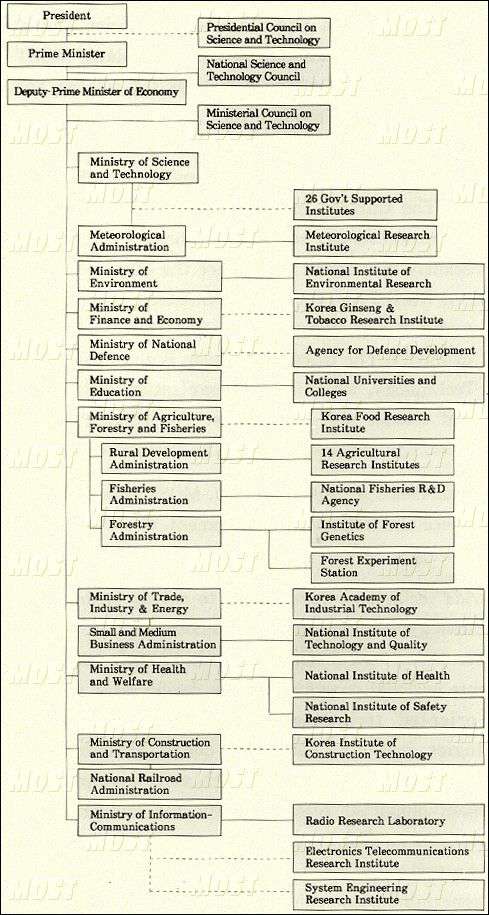
The Ministry of Science and Technology(MOST) has the responsibility of
formulating national science and technology policies and plans. In the
process of formulating the national development plans, MOST coordinates
and integrates the plans of other ministries for science and technology
development through three mechanisms. One of the mechanisms is the
National Science and Technology Council, which coordinates and integrates
inter-ministerial execution and operates under the chairmanship of the
Prime Minister. The thirteen ministers and distinguished persons in the
field of science and technology serve as members of the Council. The second
mechanism, recently introduced to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency
of governmental R&D Program, is the Ministerial Council on Science and
Technology, under the chairmanship of the Deputy-Prime Minister for
Finance and Economy. The third mechanism is the Presidential Council on
Science and Technology, which is an organization of leaders representing
diverse areas of science and technology. The council reviews important
science and technology policies to advise the President.(Chart 1.1)
MOST was established on April 21, 1967. MOST acts as the central agency
for national science and technology development. The main functions of MOST
include the following:
-
- To provide technology forecasting to set up basic policy for science
and technology development and promotion.
- To pursue technological self-reliance in the safe use of nuclear energy.
- To execute national programs for the development of core technologies,
future- oriented technologies, big science and multidisciplinary
technologies, including aerospace, ocean, nuclear energy, etc.
- To support basic & applied research and development conducted by
government-supported research institutes, university R&D centers,
and private sector R&D centers.
- To build a policy for R & D investment, human resources, information,
and international cooperation in science and technology.
- To promote the public's understanding of science and technology, etc.
Science and Technology Administration
Legal Framework
There are about ninety laws in force for science and technology development and promotion. Of them, major laws are:
- The National Science and Technology Promotion Law (Law No. 1864,
1967)
This is the basic law to systematically promote science and technology
at the national level. The important provisions of this law include the
establishment of policies and plans for science and technology and the
overall support mechanism for related projects and agencies.
- The Industrial Technology Development Promotion Law(Law No 2399,1972)
This law provides financial and tax incentives to encourage technology
development of private enterprises.
- The Promotion of Engineering Services Law (Law No. 2474, 1973)
This law aims to promote the engineering industry, which contributes
to the development of manufacturing industies and expedites the
commercialization of R&D results.
- The Promotion of Basic Scientific Research Law (Law No. 4196, 1989)
This law provides a legal base for financial support for basic scientific
research at R & D institutes and universities.
- The Atomic Energy Law (Law No. 483, 1959)
This law was enacted to promote the peaceful use of atomic energy. It
also includes measures regarding radiation disaster and public safety.
- Special Law on Innovation of Science and Technology
This law is being written to greatly accelerate innovation in science
and technology. It only will be in force for five years.


